Innovations Shaping the Future of Residential Building
The construction industry stands at a pivotal moment, driven by the necessity to meet sustainability goals, improve energy efficiency, and enhance structural resilience. Emerging materials and innovative construction methods are increasingly becoming essential in shaping the future of residential building. From bio-based materials to advanced 3D printing techniques, the way we design and construct homes is undergoing a significant transformation.
The Importance of Adopting Emerging Materials
As highlighted in my recent book, the evolving International Residential Code (IRC) underscores the importance of integrating innovative materials that enhance safety, sustainability, and efficiency in construction. Materials once considered experimental—such as self-healing concrete, carbon-sequestering composites, and mycelium-based products—are rapidly gaining acceptance within mainstream residential projects.
Innovative Construction Materials Transforming the Industry
Self-Healing Concrete
Self-healing concrete represents a major advancement in building durability. Embedded capsules containing bacteria and nutrients activate when moisture penetrates cracks, naturally producing limestone to repair the structure. This technology reduces maintenance costs, increases building longevity, and improves overall resilience against environmental stresses.
Mycelium-Based Materials
Mycelium, the root structure of mushrooms, is now engineered into high-performing insulation and structural panels. With a low Global Warming Potential (GWP), materials like MycoWood contribute significantly to sustainable construction, providing excellent insulation and soundproofing capabilities without harmful emissions.
Transparent Wood
Transparent wood is an innovative alternative to traditional glass. By treating wood with special resins, this material achieves impressive strength, flexibility, and thermal efficiency. Transparent wood not only contributes to better insulation but also significantly reduces the environmental impact compared to conventional glass production.
Sustainable Solutions in Residential Construction
Integrating sustainable materials aligns closely with evolving IRC standards. Products such as lightweight aggregates, bio-based insulation like MykoFoam, and recycled façade materials exemplify how builders can achieve compliance while minimizing environmental impact.
Bio-Based and Recycled Materials
Bio-based materials like straw panels and recycled plastic façades, such as Pretty Plastic’s rPVC tiles, are redefining what it means to build sustainably. These products effectively reduce carbon footprints, decrease waste, and utilize circular economy principles, resonating with modern regulatory and market demands.
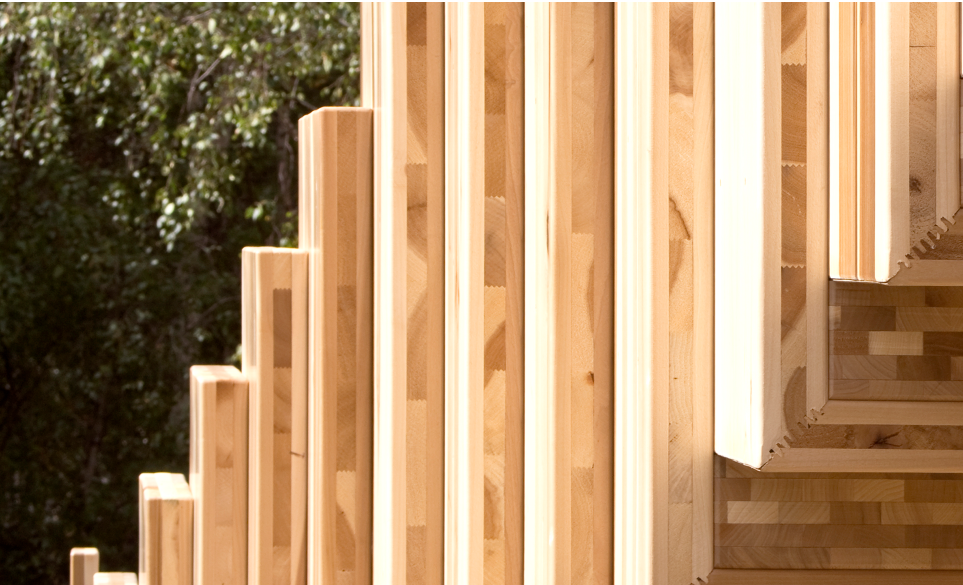

Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
Cross-laminated timber is a prime example of a sustainable, structurally sound alternative to steel and concrete. With significant carbon-sequestration capabilities, CLT provides robust, fire-resistant solutions suitable for both residential and commercial buildings.
Emerging Construction Methods Revolutionizing the Industry
Emerging materials alone aren’t sufficient; innovative construction methods are equally critical for advancing the industry’s standards and efficiencies.
3D-Printed Homes
3D-printed construction methods are rapidly transforming the residential landscape. Recognized by recent IRC updates, 3D printing techniques enable fast, cost-effective, and customizable construction, significantly reducing material waste and labor costs.
Cob and Alternative Natural Construction Methods
Cob construction, using a mixture of clay, sand, straw, and water, is gaining regulatory recognition. This method aligns closely with the IRC’s sustainability goals, offering energy-efficient homes with natural thermal mass properties ideal for passive heating and cooling.
Balanced Ventilation Systems
The IRC’s acceptance of reduced airflow requirements for balanced ventilation underscores the importance of advanced mechanical systems in modern construction. These systems ensure efficient energy use while maintaining optimal indoor air quality, directly enhancing occupant health and comfort.
Practical Integration and Regulatory Compliance
As an architect and economist specializing in residential building codes, I understand the practical challenges builders face integrating these advanced materials and methods. Training, supply chain adaptation, and cost management are critical. However, the long-term benefits—lower operational costs, improved structural resilience, and enhanced sustainability—far outweigh the initial investments.
Builders, architects, and engineers must collaborate closely to navigate regulatory frameworks effectively, ensuring that innovative approaches align seamlessly with the latest IRC provisions.
Building the Future
Emerging materials and construction methods are not merely trends; they represent a fundamental shift toward sustainability, resilience, and innovation in residential construction. By embracing advanced materials like mycelium composites, self-healing concrete, and revolutionary methods such as 3D printing and cob construction, we are not only complying with evolving building codes but also setting the stage for safer, more sustainable, and efficient housing for future generations.
As professionals in this rapidly evolving field, our commitment to continuous learning and adaptation will determine our industry’s capacity to meet tomorrow’s challenges effectively.